Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI), one concept stands out for its transformative potential: AI agents. These intelligent autonomous systems are changing the way we interact with technology, automate tasks, and solve complex problems. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to AI agents, explaining what they are, how they work, and their impact on various industries. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of AI agent technology and its significance in today’s digital landscape.
What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a software entity that autonomously performs tasks on behalf of a user or another program, utilizing AI techniques to make decisions and learn from experience. These agents interact with their environment by perceiving information through sensors, processing that information, and acting upon the environment using actuators to achieve specific, predetermined goals. While humans set the objectives, AI agents independently determine the best actions to accomplish them.
AI agents are capable of collecting data from their surroundings, learning from it, and adapting their behavior accordingly. For example, consider an AI agent in a contact center designed to resolve customer queries. It automatically engages with customers by asking pertinent questions, searches internal documents for relevant information, and provides solutions. Based on the customer’s responses, the agent decides whether it can resolve the issue independently or if it should escalate the query to a human representative.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
The key characteristics of an AI agent encompass several fundamental aspects that enable it to operate effectively and intelligently within its environment. Most of AI agents will include some if not all core characteristics:
Autonomy: AI agents operate without continuous human intervention, making decisions and performing tasks independently. This allows them to function in dynamic environments and handle complex tasks without needing constant oversight.
Reactivity: They can perceive and respond to changes in their environment in real-time. This ability ensures that AI agents can adapt to new information or unexpected situations, adjusting their actions accordingly to remain effective.
Proactiveness: Beyond just reacting, AI agents take the initiative to achieve their goals. They can plan ahead, anticipate future states of the environment, and act to influence outcomes in their favor.
Social Ability: AI agents often need to interact with other agents or humans. This involves communication, cooperation, negotiation, and sometimes competition, enabling them to function in multi-agent systems or assist users effectively.
Learning: Through experience and data analysis, AI agents improve their performance over time. Learning enables them to refine their strategies, adapt to new patterns, and become more efficient in achieving their objectives.
Rationality: AI agents are expected to act rationally, choosing actions that maximize their chances of success based on the information available. Rationality involves logical reasoning and decision-making processes that align with their goals.
Types of AI Agents
Intelligent agents can be classified into various types based on a wide range of criteria. Here are some examples of different types of AI agents.
1, Intelligence Complexity Types
Simple Reflex Agents
Description: Operate solely on current perceptions, following predefined rules without considering past experiences.
Examples:
- Thermostats: Adjust temperature based on current readings.
- Basic Chatbots: Respond to specific keywords without understanding context.
Use Cases: Ideal for straightforward tasks in fully observable environments.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Description: Maintain an internal state to track unobservable aspects of the environment, allowing for more informed decisions.
Examples:
- Autonomous Vacuum Cleaners: Map rooms to navigate efficiently.
- Traffic Control Systems: Adjust signals based on traffic patterns.
Use Cases: Suitable for partially observable environments where agents need to infer missing information.
Goal-Based Agents
Description: Act to achieve specific objectives, using planning and search algorithms to determine the best actions.
Examples:
- Chess Programs: Plan several moves ahead to win the game.
- Logistics Systems: Optimize delivery routes for efficiency.
Use Cases: Best for complex tasks requiring strategic planning and decision-making.
Utility-Based Agents
Description: Make decisions based on a utility function, aiming to maximize overall satisfaction or performance.
Examples:
- AI Trading Systems: Balance risk and reward to maximize returns.
- Recommendation Engines: Personalize content to enhance user satisfaction.
Use Cases: Useful when balancing multiple goals and uncertainties is necessary.
Learning Agents
Description: Improve over time by learning from experiences and adapting to new situations.
Examples:
- Image Recognition Systems: Increase accuracy with more data.
- Game-Playing AI: Learn strategies through reinforcement learning.
Use Cases: Essential in dynamic environments where adaptability is crucial.
2, Environmental Interaction Types
Passive Agents
Description: Observe the environment without affecting it, used primarily for monitoring and analysis.
Examples:
- Weather Prediction Models: Forecast weather by analyzing data.
- Market Analysis Tools: Monitor trends without influencing them.
Use Cases: Ideal for data collection and observation without direct intervention.
Active Agents
Description: Interact with and modify their environment to achieve goals.
Examples:
- Industrial Robots: Assemble products in manufacturing.
- Virtual Assistants: Perform tasks based on user commands.
Use Cases: Suitable for tasks requiring direct action to influence outcomes.
3, Embodiment Forms Types
Software Agents
Description: Exist entirely in digital environments, handling data processing and virtual tasks.
Examples:
- Web Crawlers: Index internet content for search engines.
- Algorithmic Trading Bots: Execute trades in financial markets.
Use Cases: Ideal for tasks within computer systems, like data analysis and virtual interactions.
Robotic Agents
Description: Have a physical presence, combining AI with mechanical components to interact with the real world.
Examples:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Navigate roads and traffic.
- Humanoid Robots: Assist in customer service or research.
Use Cases: Necessary when physical interaction with the environment is required.
4, Cooperation Dynamics Types
Single Agents
Description: Operate independently without coordination with others.
Examples:
- Personal AI Assistants: Manage schedules and reminders.
- Automated Customer Service Bots: Handle individual queries.
Use Cases: For tasks that can be completed without collaboration.
Multi-Agent Systems
Description: Multiple agents work together or compete to achieve goals, requiring coordination and communication.
Examples:
- Swarm Robotics: Coordinate for search and rescue operations.
- Economic Simulations: Model interactions between market participants.
Use Cases: Ideal for complex, distributed problems benefiting from collaboration.
5, Adaptability Level Types
Static Agents
Description: Have fixed capabilities and do not learn or adapt over time.
Examples:
- Rule-Based Expert Systems: Provide consistent diagnoses based on predefined rules.
- Fixed Game AI Opponents: Offer a constant level of challenge without adapting.
Use Cases: Appropriate when consistent behavior is desired in stable environments.
Adaptive Agents
Description: Modify their behavior based on experience and feedback, learning from interactions.
Examples:
- Recommendation Systems: Adjust suggestions based on user preferences.
- Adaptive Control Systems: Optimize industrial processes over time.
Use Cases: Necessary in environments where change is constant and flexibility leads to better outcomes.
6, Specialized Agent Types
Proactive Agents
Description: Anticipate needs and act autonomously without explicit instructions, enhancing efficiency by acting ahead of time.
Examples:
- Predictive Maintenance Systems: Schedule repairs before equipment fails.
- Personalized Marketing Bots: Send targeted offers based on predicted interests.
Use Cases: Valuable in dynamic environments where foresight can prevent problems or capitalize on opportunities.
Hierarchical Agents
Description: Organized in tiers, with higher-level agents coordinating lower-level ones by deconstructing complex tasks into simpler sub-tasks.
Examples:
- Multi-Level Planning Systems: Strategic decisions made at higher levels, operational tasks handled below.
- Complex Robotics Systems: High-level goals broken down into specific actions.
Use Cases: Ideal for managing complex systems requiring coordination across different levels.
Generative AI Agents
A specialized type of AI agent is the generative AI agent, which is designed to produce new content or data based on learned patterns from existing information. Generative AI agents expand the capabilities of AI by not only performing tasks but also generating novel content, demonstrating a form of creativity that mirrors human-like innovation. Unlike traditional AI systems that follow predefined rules, generative AI agents can create original outputs across various domains:
Text: Writing articles, stories, or reports.
Images: Generating artwork or realistic images.
Music: Composing original songs or soundtracks.
Code: Writing software programs or scripts.
Agents Variety
The variety of AI agents reflects the diverse challenges and applications they are designed to address. From simple reflex agents handling straightforward tasks to learning agents that adapt and evolve, each type offers unique advantages. By understanding these categories, developers and businesses can select the most appropriate AI agents to meet their specific needs, driving innovation and efficiency across industries.
As AI technology continues to advance, the lines between these categories may blur, leading to more sophisticated and hybrid agents capable of tackling even more complex problems. Embracing the full spectrum of AI agent types will be essential in harnessing the true potential of artificial intelligence.
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents are transforming the way we simplify and automate complex tasks across various industries. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, these agents can perceive their environment, make decisions, and perform actions to achieve specific goals—all with minimal human intervention. Let’s explore how AI agents operate and the key processes that enable them to function effectively.
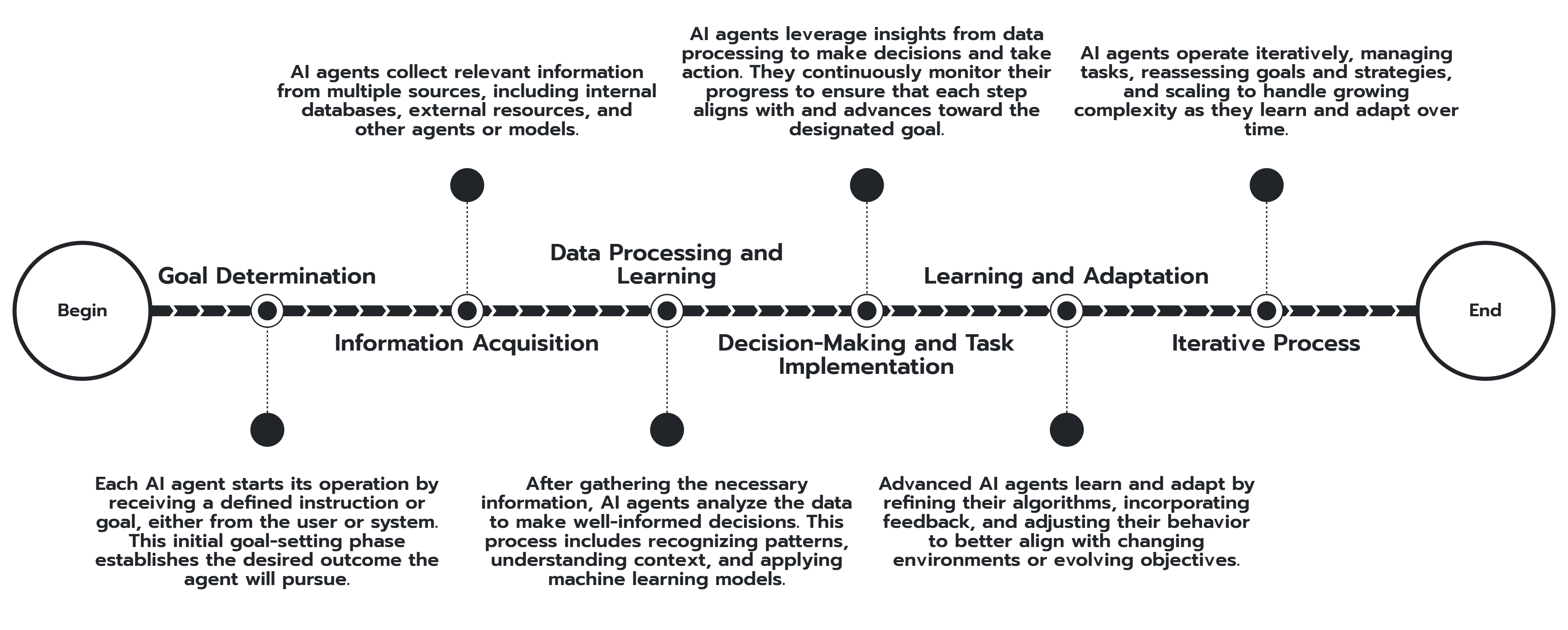
Goal Determination
Every AI agent begins its operation by receiving a specific instruction or goal from the user or system. This goal-setting phase is crucial as it defines the desired outcome the agent aims to achieve. The agent:
- Plans Tasks: Uses the goal to devise a plan that will lead to a relevant and useful outcome.
- Breaks Down Goals: Decomposes the overarching goal into smaller, actionable tasks.
- Prioritizes Actions: Determines the order or conditions under which tasks should be performed to efficiently reach the objective.
Example: An AI agent tasked with managing customer support might set goals like reducing response time or increasing customer satisfaction, then break these down into tasks such as categorizing inquiries or prioritizing urgent issues.
Information Acquisition
To effectively perform its tasks, an AI agent needs access to relevant information. It gathers data from various sources, which may include:
- Internal Databases: Accessing existing company records or customer data.
- External Sources: Searching the internet or social media for additional information.
- Other Agents or Models: Interacting with other AI agents or machine learning models to exchange data.
Example: An AI agent analyzing customer sentiments might extract conversation logs, scan social media posts, or pull data from customer feedback forms.
Data Processing and Learning
Once the necessary information is acquired, the AI agent processes the data to make informed decisions:
- Pattern Recognition: Uses algorithms to identify patterns, trends, or anomalies in the data.
- Understanding Context: Learns context, style, and structure to better interpret information.
- Machine Learning: Employs machine learning models to improve its performance over time.
Generative AI Agents: These specialized agents generate new content—such as text, images, or music—by learning from existing data and creating outputs that mimic learned patterns, often adding a degree of randomness to enhance creativity.
Example: A generative AI agent might analyze thousands of artworks to create a new piece of art that reflects similar styles and themes.
Decision-Making and Task Implementation
Armed with insights from data processing, the AI agent proceeds to:
- Make Decisions: Applies decision-making algorithms to choose the best course of action for each task.
- Implement Actions: Methodically performs tasks, adjusting as necessary based on real-time feedback.
- Evaluate Progress: Continuously checks if the actions are moving toward achieving the designated goal.
Example: In a retail setting, an AI agent may decide to offer personalized product recommendations based on a customer’s browsing history and purchasing patterns.
Learning and Adaptation
A hallmark of advanced AI agents is their ability to learn and adapt:
- Continuous Improvement: Refine algorithms by learning from new data and past experiences.
- Feedback Integration: Use external feedback and internal performance metrics to adjust strategies.
- Adaptation: Modify behavior to better suit changing environments or evolving goals.
Example: A customer service chatbot learns from each interaction, improving its responses and becoming more effective at resolving customer inquiries over time.
Iterative Process
The operation of an AI agent is often iterative:
- Task Management: Removes completed tasks from its list and may add new ones as needed.
- Reassessment: Regularly reassesses goals and strategies to ensure alignment with desired outcomes.
- Scalability: Capable of handling increasing complexity as it learns and adapts.
Example: An AI agent managing supply chain logistics might continually optimize routes and delivery schedules based on traffic patterns, weather conditions, and shipment priorities.
AI agents work through a cyclical process of goal setting, information gathering, data processing, decision-making, and learning. By automating these steps, they simplify complex tasks and improve efficiency across various applications. Their ability to learn and adapt makes them increasingly valuable in a world where data is abundant, and timely decision-making is crucial.
Whether it’s generating creative content, providing personalized customer experiences, or optimizing business operations, AI agents are at the forefront of technological innovation, driving progress and opening new possibilities.
What are the benefits of using AI agents?
AI agents are revolutionizing the way businesses operate and how customers interact with products and services. These autonomous intelligent systems perform specific tasks without human intervention, offering a multitude of benefits across various industries. From increasing efficiency to fostering innovation, AI agents are becoming indispensable tools for organizations aiming to stay competitive in today’s dynamic market. Let’s explore the key advantages of integrating AI agents into your business operations.
Increased Efficiency
AI agents excel at automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, performing them faster and more accurately than humans. By handling routine processes, they allow professionals to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. This shift not only boosts productivity but also leads to higher job satisfaction as employees engage in more meaningful activities.
Cost Reduction
Automating processes with AI agents can significantly lower operational costs. By reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing errors arising from human intervention, businesses can improve profit margins and enhance overall sustainability. This cost efficiency is particularly impactful in industries like manufacturing, design, and logistics.
Scalability
One of the standout benefits of AI agents is their ability to handle increased workloads without a proportional increase in resources. They operate continuously—24/7—without fatigue, allowing organizations to scale their operations quickly. This flexibility enables businesses to adapt to changing market demands and provides a competitive edge in fast-paced environments.
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
Generative AI agents bring a new dimension to creativity by providing fresh ideas and perspectives. They can inspire human creators to develop innovative solutions, resulting in groundbreaking products and services. This synergy between AI and human ingenuity fosters an environment where innovation thrives, leading to unique offerings that set a business apart in the market.
Data-Driven Insights for Informed Decision-Making
Advanced AI agents utilize machine learning to gather and process vast amounts of real-time data. They uncover patterns and insights that inform better decision-making, enabling business managers to make accurate predictions swiftly. For example, AI agents can analyze product demand across different market segments, helping to optimize marketing strategies and improve campaign effectiveness.
Personalization and Improved Customer Experience
Today’s customers expect personalized and engaging interactions. AI agents enable businesses to tailor products and services to individual preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. By providing prompt responses and customized recommendations, AI agents improve customer engagement, boost conversion rates, and foster long-term relationships.
Flexibility and Adaptability
AI agents follow consistent models that adapt to changing environments, allowing businesses to perform complex tasks confidently. Their ability to learn and evolve ensures that operations remain efficient even as conditions shift. This adaptability reduces unnecessary costs associated with process inefficiencies and keeps businesses agile in the face of change.
Integrating AI agents into businesses can transform operations, reduce costs, and create exceptional customer experiences. By leveraging these advanced technologies, organizations can achieve their goals more efficiently and effectively, driving greater return on investment and fostering long-term success.
Challenges of Using AI Agents
While AI agents offer transformative benefits—such as increased efficiency, cost savings, scalability, and personalized experiences—they also present significant challenges that organizations must carefully consider. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for businesses aiming to integrate AI agents successfully into their operations. Let’s delve into the key challenges associated with deploying AI agents and their implications.
1. Ethical Concerns and Bias
AI agents rely heavily on data to make decisions. If the data they are trained on contains biases, the agents may inadvertently perpetuate unfairness or discrimination. Issues related to privacy, bias, and transparency in decision-making raise ethical questions that organizations must address. For example:
- Bias in Decision-Making: An AI agent used in recruitment might discriminate against certain groups if historical biases are present in the training data.
- Lack of Transparency: Complex AI models can act as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific decisions.
Solution: Implementing safeguards such as regular audits, ethical guidelines, and human oversight ensures that AI agents make fair and transparent decisions.
2. Data Privacy and Security Risks
Developing and operating advanced AI agents requires collecting, storing, and processing vast amounts of sensitive data. This dependence on data introduces significant privacy and security risks:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to data can lead to severe reputational damage and legal repercussions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA requires meticulous data handling and user consent practices.
Solution: Strengthen data security measures, ensure compliance with regulations, and adopt robust encryption and access control protocols.
3. Technical Complexity and Resource Requirements
Implementing AI agents involves substantial technical complexity, requiring specialized expertise in machine learning, data engineering, and natural language processing:
- Skill Gap: Many organizations lack the in-house talent needed to develop and maintain advanced AI systems.
- Infrastructure Costs: Training AI agents demands significant computational resources, which can be cost-prohibitive for small to medium-sized businesses.
Solution: Invest in talent acquisition or partnerships with specialized firms, and consider scalable cloud-based solutions to mitigate infrastructure costs.
4. Limited Computing Resources
Training and deploying AI agents, especially those using deep learning models, require substantial computing power:
- On-Premise Challenges: Organizations opting for on-premise solutions face high costs in hardware investment and maintenance.
- Scalability Issues: Scaling up operations can be difficult without flexible infrastructure.
Solution: Utilize cloud computing services that offer scalable resources and consider hybrid models that balance on-premise and cloud solutions.
5. Integration with Existing Systems
For businesses operating with legacy systems, integrating AI agents can be daunting:
- Compatibility Issues: AI agents may not be compatible with outdated technologies.
- Cost of Upgrades: Upgrading existing systems to support AI functionality can be expensive and time-consuming.
Solution: Develop a strategic integration plan, possibly adopting a phased approach, and ensure that new AI systems are interoperable with existing infrastructure.
6. Job Displacement and Economic Impact
The automation capabilities of AI agents raise concerns about job displacement:
- Reduced Demand for Certain Roles: Tasks traditionally performed by humans may become automated, leading to workforce reductions.
- Employee Morale: Fear of job loss can affect employee morale and productivity.
Solution: Invest in employee retraining and upskilling programs to transition staff into new roles that complement AI technologies.
7. Regulatory Compliance
The rapid advancement of AI technologies has outpaced the development of comprehensive laws and guidelines:
- Uncertain Legal Landscape: Organizations may struggle to ensure compliance with existing laws while anticipating future regulations.
- Ethical Use: There’s a need for clear policies governing the responsible use of AI.
Solution: Stay informed about regulatory developments, engage with industry bodies, and implement internal policies that promote ethical AI use.
8. Security Vulnerabilities
AI agents can introduce new security vulnerabilities:
- Target for Cyberattacks: AI systems may become targets for hacking or malicious exploitation.
- System Integrity: Compromised AI agents can lead to broader system failures.
Solution: Implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular security assessments, intrusion detection systems, and incident response plans.
Addressing the Challenges
Successfully integrating AI agents requires a proactive and holistic approach:
- Ethical Frameworks: Develop and adhere to ethical guidelines that govern AI development and deployment.
- Data Governance: Establish strong data governance policies to manage data privacy and security effectively.
- Continuous Learning: Invest in ongoing education for your team to keep pace with technological advancements.
- Collaborative Approach: Encourage collaboration between technical experts, legal advisors, and business strategists to align AI initiatives with organizational goals.
The Future of AI Agents
Intelligent agents in AI are on the cusp of becoming integral to both our digital and physical worlds, supporting professional and personal tasks with unprecedented efficiency. Driven by rapid advancements in machine learning, data availability, and computational power, AI agents are set to become smarter, more adaptable, and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. Here’s a glimpse into how AI agents will shape the future across various sectors.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of AI Agents
-
Enhanced Learning Capabilities: Future AI agents will learn more efficiently, requiring less data to achieve higher levels of performance. This advancement will make AI more accessible and effective across a broader range of applications.
-
Greater Autonomy: With increased ability to make complex decisions without human intervention, AI agents will handle sophisticated tasks and adapt to new situations in real-time, boosting productivity and efficiency.
-
Collaborative AI: Instead of replacing humans, AI agents will work alongside us, enhancing our capabilities and allowing us to focus on creative, strategic, and human-centric activities.
-
Emotional Intelligence: Advanced AI agents will recognize and respond to human emotions, providing more empathetic interactions and improving customer experiences.
-
Integration Across Devices: AI agents will operate seamlessly across various platforms and environments, offering consistent support whether on smartphones, computers, or other smart devices.
AI Agents as Digital Work Companions
In the coming years, AI agents are expected to become essential digital work companions. They will assist with routine tasks such as managing emails, organizing schedules, and conducting online research. By handling these time-consuming activities, AI agents will free up employees to focus on more meaningful work, enhancing productivity across industries. They could act as personal project managers, reminding users of deadlines, prioritizing tasks, and providing data insights for better decision-making.
Transforming Customer Experiences
AI agents are set to revolutionize customer service by providing hyper-personalized, seamless experiences. With advanced natural language processing and emotion recognition, they will understand and respond to human emotions with empathy. For example, an AI customer service agent might detect a customer’s frustration and adjust its tone and solutions accordingly, leading to more satisfying interactions. As these capabilities evolve, AI-driven customer support tools will reshape how brands connect with their audiences.
Advancing Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, AI agents have transformative potential. They will assist in diagnosing patients, managing medical records, and offering initial treatment recommendations. By analyzing vast amounts of medical data, AI agents can help healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses based on a patient’s medical history and symptoms. They might serve as virtual healthcare assistants, supporting doctors in clinical decision-making or assisting patients in managing chronic conditions from home, ultimately delivering better and more efficient patient care.
Empowering Financial Decision-Making
AI agents will play an increasingly important role in the finance industry by assisting with complex data analysis, risk assessment, and customer service. They will offer real-time insights for investors and automate compliance and fraud detection processes. AI agents could operate as virtual financial advisors, providing personalized advice by analyzing spending patterns, investment portfolios, and financial goals. This AI-driven decision-making will allow financial institutions to offer more tailored services, meeting the demands of an increasingly digital-first customer base.
Elevating Education
The future of education is being shaped by AI agents that can act as personalized tutors, guiding students based on individual learning preferences and areas for improvement. As e-learning grows in popularity, AI agents will serve as digital mentors, assessing student progress in real-time and providing targeted feedback. They will transform how we acquire skills, allowing learners of all ages to study more effectively and in a personalized manner, particularly impacting online education platforms.
Supporting Environmental Solutions
With growing environmental concerns, AI agents are anticipated to play an active role in monitoring ecosystems, predicting weather patterns, and aiding in resource conservation. By processing large datasets collected from satellites, IoT sensors, and research labs, they can track climate changes and make informed predictions. AI agents will provide insights for sustainable decision-making in industries like agriculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation, helping predict and mitigate climate-related disasters.
Advancing Autonomous Systems
AI agents will significantly impact the development of autonomous vehicles and robotics. In transportation, they could operate vehicles autonomously, creating safer and more efficient travel experiences by monitoring road conditions and making real-time decisions. In manufacturing, AI agents are expected to operate complex robotics systems, optimizing assembly lines and improving quality control. As autonomous systems advance, these AI agents will enhance efficiency and safety across various industries.
Transforming Diverse Industries
From software engineering to data analytics, many sectors are poised to be transformed by AI agents. As AI technology continues to advance at breathtaking speed, the range of human activities that can be augmented or automated by AI agents will rapidly expand. Tasks currently handled by professionals like lawyers, journalists, policymakers, and researchers could see significant AI integration, reshaping these professions in ways we are just beginning to understand.
Embracing an AI-Driven Future
AI agents are not just another overhyped buzzword; they represent the inevitable evolution of artificial intelligence systems. Developing responsible and ethical AI agents will be key to ensuring these technologies benefit society as a whole. Soon, interacting with various AI agents on a daily basis will become the norm, profoundly impacting how we live and work.
The journey ahead promises to be both exciting and transformative. As AI agents continue to grow in capability and integration, they will open up possibilities we are only beginning to imagine. Embracing this future means preparing for a world where technology and humanity work hand in hand to achieve greater heights.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a monumental leap in technology, transforming how we interact and automate processes. They redefine business operations, streamline workflows, and open new avenues for growth and strategic decision-making.
As we enter a new technological era, integrating AI agents becomes crucial. They enhance efficiency and decision accuracy, giving businesses a competitive edge. Soon, daily interaction with AI agents will be the norm, profoundly influencing how we live and work.
Embracing this future prepares us for a world where technology and humanity collaborate to achieve greater heights. For companies aiming to thrive, leveraging AI agents is essential. By adopting these solutions, organizations not only keep pace but set the pace, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
In conclusion, developing responsible and ethical AI agents ensures these technologies benefit society as a whole. By embracing their transformative power, we position ourselves at the forefront of innovation, ready to harness the full potential of this exciting frontier.
Contact us for assistance with AI Agent development.
At CBBSOFT, we are here to help with your queries. Reach out today, and we will be happy to assist you.


